Financial, Fresh graduate, Young Adult
A Beginner’s Guide in Investing
Understanding Investing
What is investing? Investing is the process of purchasing assets that appreciate over time and generate returns in the form of dividends or capital gains. In a broader sense, investment can also mean devoting time or resources to bettering your own or others’ lives. Buying stocks, real estate, and other valuable items with the goal of gaining money or significant capital gains is referred to as investing in today’s business world.
Mins to Read: 13 minutes
Age: 18-21 years old

“Invest for the long-term,” once said Louis Simpson, an investment master as an executive of GEICO. Simpson and his team have consistently invested in undervalued common stocks. GEICO’s Equities have beaten the Standard & Poor’s 500 (S&P500) by an average annual gain of 6.8 percent over twenty-five years.
Remember that not all investments are suitable for beginners. Distinct sorts of investments come with different risks. “High risk, high rewards; low risk, low rewards” is the key principle of investing. In addition, investments with higher yields often need a higher initial commitment. Here is a well-known fact, you should monitor your investments regularly. Whether during a pandemic or not, it’s tempting to keep an obsessive eye on newly placed stocks, but it’s good to have a little objectivity. For example, if you’re new to stock investing, it is a good idea to check stocks at market open, noon, and close and set alerts to notify you of price drops or spikes. Timing a sale versus a purchase can be complicated, so taking the time to do some research helps.
Stop waiting till tomorrow to invest what you can today.
Here are the guides to give you information about what you need to know about investments before you start:
Why Do You Need to Invest?
Investing is an effective way to put money to good use and potentially build wealth. With smart investments, cash can outperform inflation and increase in value. Why do you need to invest? Here are some reasons:
Financial Security
People often want to be financially stable, so they need extra money. You can prepare for financial emergencies and protect yourself financially. Examples could be a significant health crisis or a costly life event such as a house destroyed by a fire. Investing ensures that you are financially covered against such unforeseen or emergency circumstances.
As a famous saying “be careful not to put all your eggs in one basket”; instead, spread your money across multiple investments to create a diversified portfolio. If your investment fails, you won’t lose all your money.
Build Your Wealth
People mainly invest in building wealth. It means you can save and then invest your savings over time—whether dividends or interest income can be reinvested in the same financial instrument or another. What you shouldn’t do is panic and sell at the first sign of loss. This crystallizes previous losses and makes it less likely that growth will be regained. So start investing and keep growing your wealth.
Achieve Your Goals
Some people set specific goals in life and invest in achieving those goals. For example, if your dream is to buy a house, or a new car, or travel the world, the goals you set will motivate you to invest. It is essential to list your goals and how much money you will need to reach them. Plans can be short-term, medium-term, or long-term. By investing your money according to your goals, you can grow your money and achieve your goals quickly without having to work for the rest of your life.
What Are The Basic Types of Investments & Their Risks?
Investors mainly invest in four main assets/securities to get appreciation: stocks, bonds, commodities, and real estate. A mutual fund is a pooling of money from investors used to buy these securities. Lastly, investment banking provides services to large corporations and institutional investors.
Stocks
Stocks are shares of an ownership interest in a company. A stock market is a place where stocks are bought and sold. The Philippine Stock Exchange (PSE) is the organization that manages our stock market. When you purchase or invest in shares, you become a partner or shareholder in that particular company.
People buy or invest in stocks to profit from a company’s great potential for long-term value. However, it also means that if the company performs poorly or suffers a loss, we may lose some of our investment.
Example:
| Date | Open | High | Low | Close |
| 21-03-2019 | 1549 | 1680.50 | 1500 | 1620.72 |
| 21-04-2019 | 1790.20 | 1921.31 | 1760 | 1877.23 |
You purchased 100 shares on the 21st of March 2019 at Php 1549. So you had to spend 100 x 1549 = Php 154,900.
As the price went up on the 21st of April 2019, you decided to sell them at the end of the day at the closing price of Php 1877.23 and receive 100 x 1877.23 = Php 187,723.
The gain in the transaction is Php 187,723 – Php 154,900 = Php 32,823 which is 21.19%.
Bonds
A bond is a fixed-income security that represents a loan made by an investor to a corporation, government, or government agency (the issuer). Companies, municipalities, and governments use bonds to finance projects and operations. Bondholders are investors that are considered creditors of the issuer.
When an investor buys a bond, they lend money to the issuer to pay back the interest and principal when the bond matures. However, inflation can erode the buying power of money and the value of a bond’s returns. Inflation has the most significant effect on fixed bonds, which have a set interest rate from inception.
Example:
If a company issues a 10-year bond with a face value of Php 10,000 and a coupon rate of 5%.
You agree to buy that bond, which will return 5% (Php 500 each year) over ten years.
At the end of the maturity date, the company will repay your Php 10,000.
That means your bond’s total expected future cash flow is Php 5,000.
Commodities
Commodities are raw materials such as corn, flour, oil, energy, and metals. Commodity trading is the buying and selling of these commodities. But often, this is done through futures contracts where you agree to buy or sell a commodity at a specific price on a particular date. Commodity trading is complex, and factors such as unpredictable weather events and political instability can hugely impact prices.
Example:
Say you are a corn farmer. So, you sell a futures contract, agreeing to sell 1,000 kilograms of corn at Php 18.62 per kilo in 60 days.
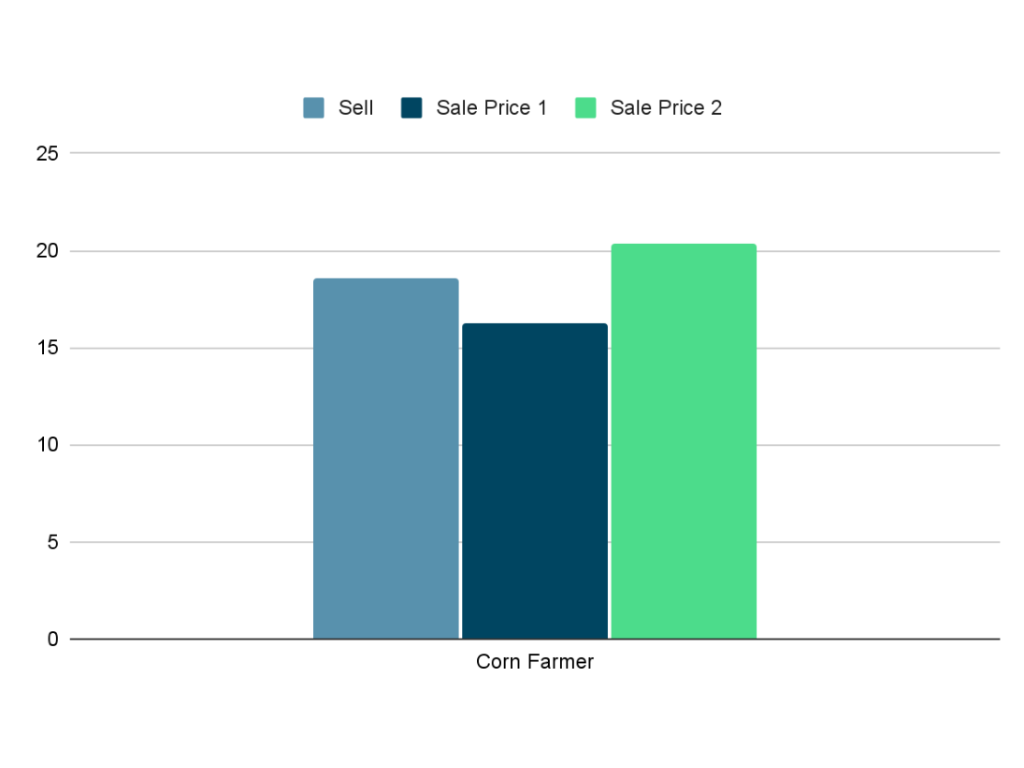
Situation #1:
You win if the sale price drops to Php 16.30 because you’ve locked in Php 18.62 per kilo.
Price Sale Computation:
16.30 x 1,000 = Php 16,300
Locked Sell Computation:
18.62 x 1,000 = Php 18,620
Profit Computation Compared to Sale Price:
18,620 – 16,300 = Php 2,320
x 100% = 12.46%
Since the sale price dropped and you locked at the price of Php 18.62 per kilo, then you have a profit of Php 2,320 which is 12.46% of the sale price.
Situation #2:
You miss out on profits if the price rises to Php 20.37 because you’ve locked in Php 18.62 per kilo.
Price Sale Computation:
20.37 x 1,000 = Php 20,370
Locked Sell Computation:
18.62 x 1,000 = Php 18,620
Profit Computation Compared to Sale Price:
18,620 – 20,370 = – Php 1,750
x 100% = -9.40%
Since the sale price raised and you locked at the price of Php 18.62 per kilo, then you have lost profit of Php 1,750 which is 9.40% of the sale price.
On the other side, say you are a food processing company that needs corn to produce cornmeal for food retailers. So, you buy that futures contract for 1,000 kilograms of corn at Php 18.62 per kilo.
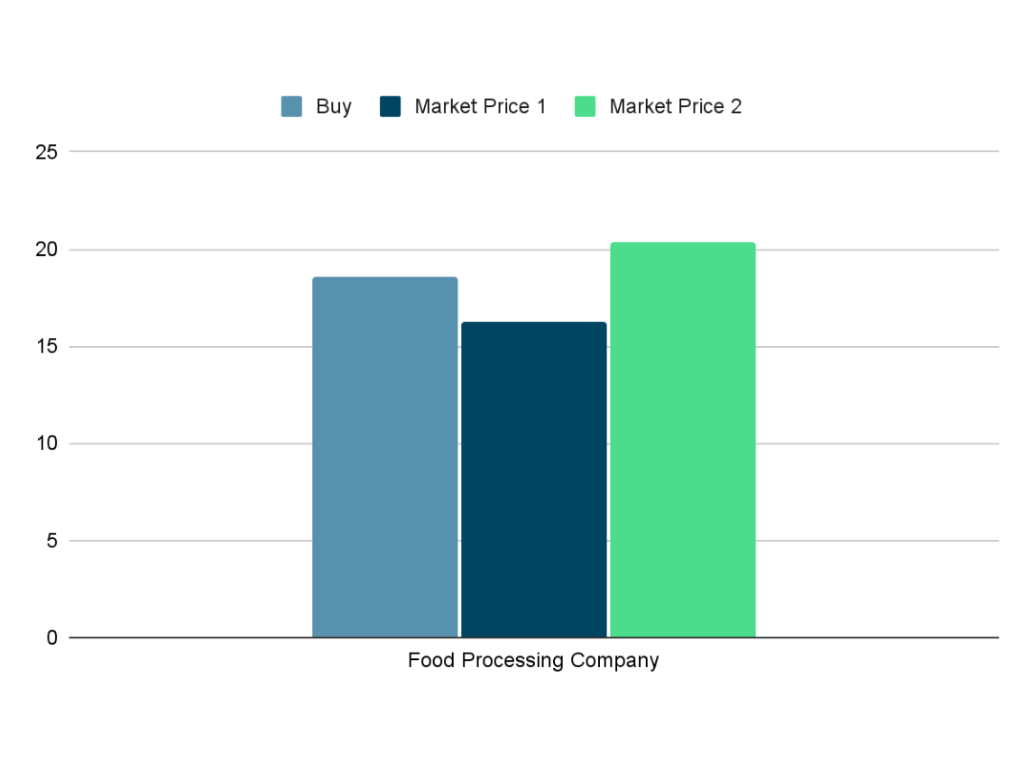
Situation #1:
If prices fall to Php 16.30, you lose because you pay more than the current market price.
Market Price Computation:
16.30 x 1,000 = Php 16,300
Locked Buy Computation:
18.62 x 1,000 = Php 18,620
Cost Computation Compared to Market Price:
16,300 – 18,620 = – Php 2,320
x 100% = -12.46%
Since the market price dropped and you locked at the price of Php 18.62 per kilo, then you have lost a total of Php 2,320 which is 12.46% of the market price.
Situation #2:
If the market price skyrocket to Php 20.37, you’re still paying only Php 18.62 per kilo.
Price Sale Computation:
20.37 x 1,000 = Php 20,370
Locked Sell Computation:
18.62 x 1,000 = Php 18,620
Cost Computation Compared to Market Price:
20,370 – 18,620 = Php 1,750
x 100% = 9.40%
Since the market price raised and you locked at the price of Php 18.62 per kilo, then you have saved a total of Php 1,750 which is 9.40% of the market price.
As an investor, you can speculate on corn prices. Say you buy that same futures contract. You have no intention of actually buying 1,000 kilograms of corn in 60 days. You are making a wager that corn prices will increase and that you can sell it for a higher price. If you think prices will decline, you might also go short.
Real Estate
When you think of real estate investing, your home is the first thing that comes to mind. Real estate investors have many other options when choosing an investment, not just physical real estate. Real estate has proven to be a solid investment opportunity in good times and bad. You can use it to protect the money you have saved for yourself and your family’s future.
Real estate investing is like finding and buying a home to live in but renting it out and collecting cash flow from the tenants. You can even buy, renovate, and flip properties for a profit if you have the time and manual labor to repair the property.
Real estate can be a solid investment with the potential to generate a steady income and build wealth. However, one of the downsides of real estate investing is its illiquidity. It is relatively difficult to convert assets into cash and cash into assets.
Example:
An apartment complex with six units. Three small rooms rent for Php 2,000 per month and the other three big rooms rent for Php 4,000 per month.
3 units * 2,000/month = Php 6,000
Php 6,000 * 12 = Php 72,000
3 units * 4,000/month = Php 12,000
Php 12,000 * 12 = Php 144,000
72,000 + 144,000 = Php 216,000 Annual income. This is the Gross Potential Income(GPI).
Mutual Fund
A mutual fund is a financial vehicle that pools the assets from its shareholders or investors for investment in securities such as stocks, bonds, commodities, real estate, and other assets. A mutual fund is managed by a professional money manager who allocates the fund’s investments and seeks to generate capital gains or income for the fund’s investors.
An investment fund is designed to offer diversification to its investors without purchasing the individual securities themselves. Investors buy shares in mutual funds. The combined holdings of a mutual fund are called a portfolio. Each share represents an investor’s partial interest in the fund and the income generated from there.
All funds carry some degree of risk. Mutual funds may lose some or all of the money invested as the securities held by the fund may depreciate. Dividend or interest payments may change as market conditions change. The higher the volatility of the fund, the higher the investment risk.
Example:
You buy 100 fund shares from Company A with a Net Asset Value(NAV) of Php 100 per share for an initial value of Php 10,000. Since Company A pays a 5% dividend you reinvest, buying five additional shares. After one year, the share price rises to Php 150.
To calculate the investment’s total return,
105 shares x Php 150 per share = Php 15,750 Current Value
15,750 – 10,000 = Php 5,750 Total Gains
x 100 = 57.5%
Your total return is 57.5%
Investment Banking
Investment banking is a type of banking that organizes large and complex financial transactions, such as mergers and underwriting initial public offerings (IPOs). The banks can raise funds for corporations in various ways, such as issuing new securities for corporations, communities, or other institutions. The bank manages your company’s IPO. They have someone to advise on mergers, acquisitions, and restructurings. They help clients find their way in the complex world of advanced finance.
Investment bank invests in various securities at all levels of the market, and as such, there are risks involved. Market risk is the utmost concern for investment banks due to variables in the market such as exchange rates, inflation, and interest rate. Exterior risk factors, such as credit risks, occur if the client fails to make interest payments or repay the principal amount after being financed by a bank.
Example:
Bank A has an annual interest rate of 4% for investment. You decide to invest your Php 10,000 for 5 years.
To calculate the total return,
10,000 x 0.04 = Php 400 interest per year
400 x 5 years = Php 2,000 total interest
10,000 + 2,000 = Php 12,000 total return
Your total return for an investment of 5 years is Php 12,000.
How to Start Investing?
Invest early and start now. It is better to start while you are still in your 20s. Every day you wait or keep your money at home, you lose the opportunity to build wealth from your investment opportunities. There will be ups and downs in investing, but investing young means you have decades to get over it — and decades for your money to grow. Start now, even if you have to start small.
You may think you need a lot of money, but you can start by investing 10,000 pesos. The first amount is not the most important thing. It will prepare you financially and allow you to invest your money more often. An essential step before investing is setting up an emergency fund. The emergency fund is the cash set aside for quick withdrawal.
Risk tolerance is one of the first things you should consider when investing. By diversification, you can reduce the risk as a long-term investor. Invest your money in a variety of investments to minimize your investment risk. If one of your investments does not perform well and you suffer a loss, you can offset that loss with your other investments for a positive or much higher return. In this way, you can reduce the loss of your investment.
It’s essential to understand each option and how much risk it carries. The most popular investments for those just starting are stocks, bonds, commodities, real estate, and mutual funds.
You can also find a financial planner who will work with you to set financial goals and personalize your trip. When looking for an advisor, you want to find someone who puts your best interests first. Ask them questions about their referrals, make sure they are acting dutifully in your best interests, and ensure you understand their payment schedule, so you don’t have to worry about hidden fees. Please do not get hit by Your investment strategy will depend on your savings goals, the amount of money you need to reach your goals, and your time horizon.
How Does Investing Work?
How investing works is by depositing money in an account or fund to earn a profit. Investment can yield greater returns (and possibly greater risk) over time. For this reason, some people use assets to achieve long-term goals such as retirement.
Where Does The Money Go?
Financial products whose value is held in an account include stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and annuities.
How Does The Money Grow?
As investments such as stocks rise or fall in value, the value of your account will change. Growth is more likely, but not guaranteed. You can also sell your investments for a profit (or loss), receive dividends on stocks, or receive interest on bonds. A common strategy for investment is to buy for a low price and sell high. You can also reinvest the income from your investment because your total investment will increase, and you will earn even more at a constant interest rate next time.
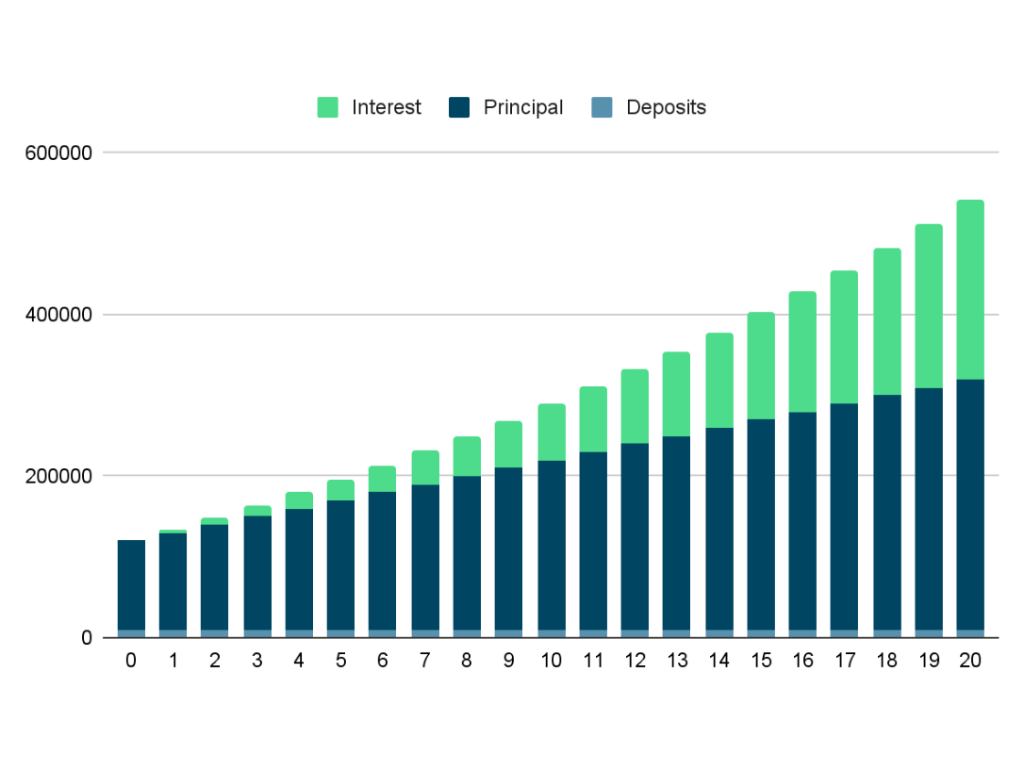
Example: Suppose you invest 100,000 pesos today. After 20 years, assuming a 7% annual return also considering the inflation rate of 3%. It means the inflation-adjusted return is 7% – 3% = 4%, so your initial investment will become 219,112.31 pesos.
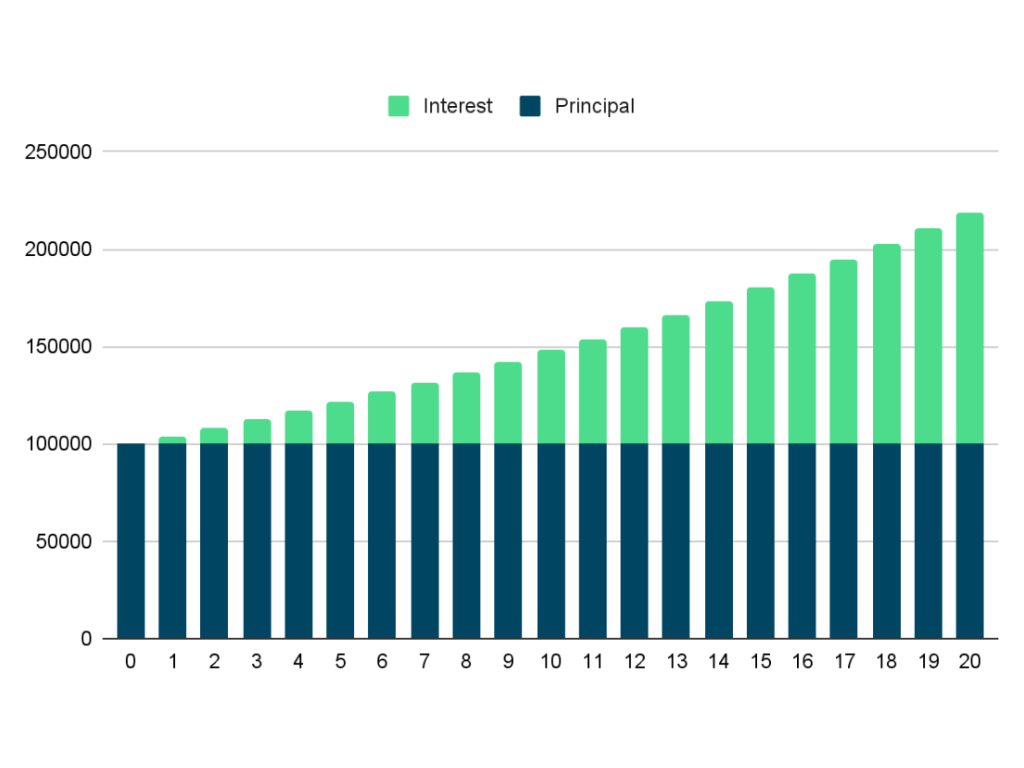
Now, suppose you invest 100,000 pesos today and contribute 10,000 pesos annually. After 20 years, assuming a 7% annual return and considering the inflation rate of 3%. It means the inflation-adjusted return is 7% – 3% = 4%, so your initial investment will be more than the first sample to 528,804.33 pesos.
Risk and Flexibility
Buying or adding is generally pretty flexible. Growth is not guaranteed, so there are more risks. Some are tax efficient. The higher the interest rate (called “yield”), the more income you can generate and reinvest. However, in general, high-yield investments are riskier. Therefore, the appropriate level of risk depends on how much you are willing to take.
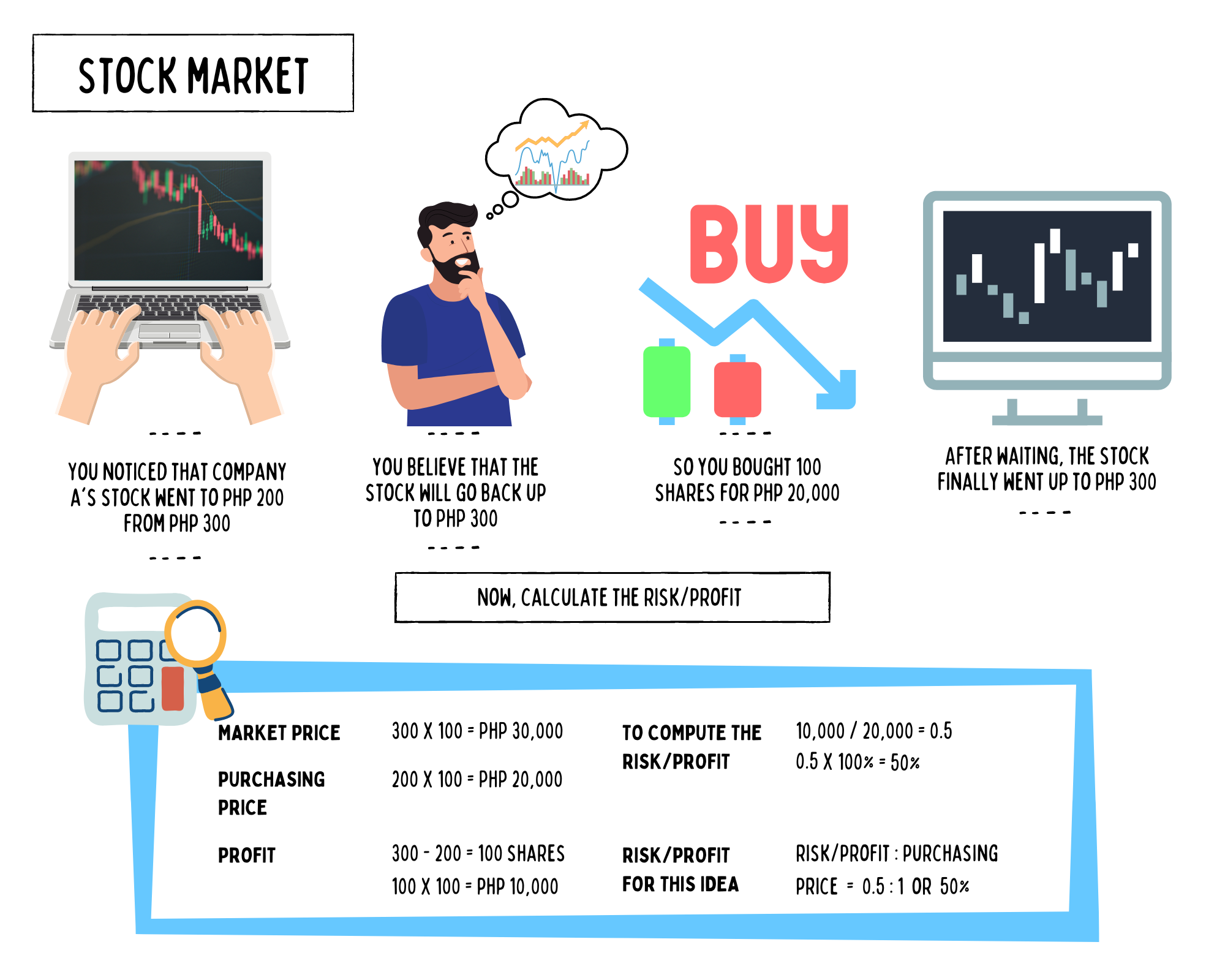
For example, you did your research and found a stock you like. You notice that Company A’s stock is trading at Php 200, down from a recent high of Php 300.
Believe that if you buy now, in the future, the stock will go back up to Php 300, and you can cash in. You have Php 20,000 to put toward this investment, so you buy 100 shares.
To calculate the risk/profit, you divide your net profit by the price of your maximum risk. If your stock went up to Php 300 per share, you would make Php 100 for each of your 100 shares for a total of Php 10,000. So, you would divide 10,000 by 20,000 which gives you 0.5.
That means that your risk/profit for this idea is 0.5:1 or 50%.
Here’s an illustration for the example above:
Investing Tips
Investment is not easy. You must learn more about investing and the ins and outs before investing in a long-term investment. Here are some tips to help you with your assets:
Invest in yourself
Make time for yourself. Before investing, protect yourself from income loss, accidents, illness, and even death. You can be in financial trouble if you do not have proper insurance. With insurance, you do not have to take early withdrawals from your investments in an emergency.
Determine your goals
Ask yourself these questions: What do you want to happen in your life? What do you want to achieve in the future? Do not invest just for the sake of it or without a plan. You need to understand your financial situation, then develop your own financial and investment strategy to improve your situation. Whatever your goal is, it should be clear from the beginning to help you make the proper adjustments and decisions.
Start small and steady
As a beginner, start with something more beginner-friendly and less risky. Go for bonds and preferred shares since they have low risks with a good return. See how the market is affecting your investments and understand your earnings. No need to be an expert. It may take time for your money to grow, but prudence pays off. Being reckless and aggressive can cost you what you worked so hard for.
Know the trend
The most important thing to do when investing is to understand the market, the investment, and the process. Build your confidence by learning the basics of investing, which will help you become a better investor. You can understand standard investment terms and words by reading reliable online articles on investing in the Philippines or watching YouTube videos on how to grow your money for a few hours a day. Stay updated on news and current events to learn and gather insights that may affect the market.
Gather your options
When you start investing, discuss your financial and investment goals with your financial advisor and feel confident considering suitable investment options. Ask your financial advisor to help you make a plan, implement strategies, and build a solid financial foundation.
Factors That Affect Investment Decisions
Interest – This risk affects investors in the form of fluctuating interest rates over the course of the investment timeline. The uncertainty surrounding the capital that an investor is most likely to blame. In other words, if the interest rate changes, so will the cost of the debt. For instance, bonds’ value decreases when interest rates do, and vice versa.
Inflation – The risk of losing one’s purchasing power is primarily the result of growing inflation. Typically, this risk affects investors when the rate of investment returns is lower than the pace of rising inflation. In other words, investors will only get a return of 2%, for instance, if the rate of return is 5% and the inflation rate is 3%. For instance, if the inflation rate is 5% and the rate of return is 3%, then you will lose 2% interest.
Volatility – This is the risk to the value of an investment, usually an options portfolio, due to unpredictable changes in the price of a stock over a particular period. The effectiveness of firms, which is frequently influenced by dormant microeconomic issues, determines the worth of these funds. The issues may include shifting governmental directives, the state of the economy, monetary policies, and other factors are among these variables.
Common Investment Terminologies
- Asset allocation – The practice of balancing your investments to limit risk.
- Capital – The budget invested in a company on a long-term basis and obtained by issuing preferred or common stock, retaining a portion of the company’s earnings from the date of incorporation, and by long-term borrowing.
- Capital gain – A profit or return of an investment.
- Capital loss – The amount by which the proceeds from a sale of a security are less than its purchase price.
- Dividend – The portion of the company’s income payout to shareholders.
- Fund – A pool of money from a group of investors in order to buy securities.
- Inflation – A rise in the prices of goods and services, often equated with a loss of purchasing power.
- Interest rate – The amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed.
- Investment advisor – An organization employed by a mutual fund to give professional advice on the fund’s investments and asset management practices.
- Liquidity – The ability to have ready access to invested money.
- Market price – The current price of an asset.
- Maturity – The date specified in a notice or bond on which the debt is due and payable.
- Net Asset Value per share (NAV) – The current value of a single mutual fund share; also known as share price.
- Portfolio – A collection of investments owned by one organization or an individual, and managed as a collective whole with specific investment goals in mind.
- Risk tolerance – The degree to which you can tolerate volatility in your investment values.
- Securities – Another name for investments such as stocks or bonds.
- Share – Also known as stocks or shares of stock, is a portion of ownership of a company’s equity.
- Short selling – Borrowing shares of stock and selling them at their current price with the promise to return the shares to the lender in the future.
- Volatility – The degree to which a traded asset varies or fluctuates in price over time.
- Yield – Annual percentage rate of return on capital. The dividend or interest paid by a company is expressed as a percentage of the current price.
MUST-READ AND SHARE!
2023 Your Practical Wedding Guide
Your Ultimate Access to Kuwait Directories in this COVID-19 Crisis
Investments and Finance Ultimate Guide
OFW FINANCE – Money News Update that you need to read (Table of Contents)
A Devotional for having a Grateful Heart
Stock Investment A Beginner’s Guide
How To Save Money Amidst Inflation
Philippines Best Banks with High-Yield Savings Return
Essentials Before Applying For a Credit Card
If you like this article please share and love my page DIARYNIGRACIA PAGE Questions, suggestions send me at diarynigracia @ gmail (dot) com
You may also follow my Instagram account featuring microliterature #microlit. For more of my artworks, visit DIARYNIGRACIA INSTAGRAM




Peace and love to you.